This is a part of the Memory Subsystem.
Basics
On an LLC (last level cache) miss, a read request for a cache line is typically sent to the memory controller. If the incoming cache line displaces a dirty line in the LLC, that dirty line has to be sent to the memory controller as a write request as well.
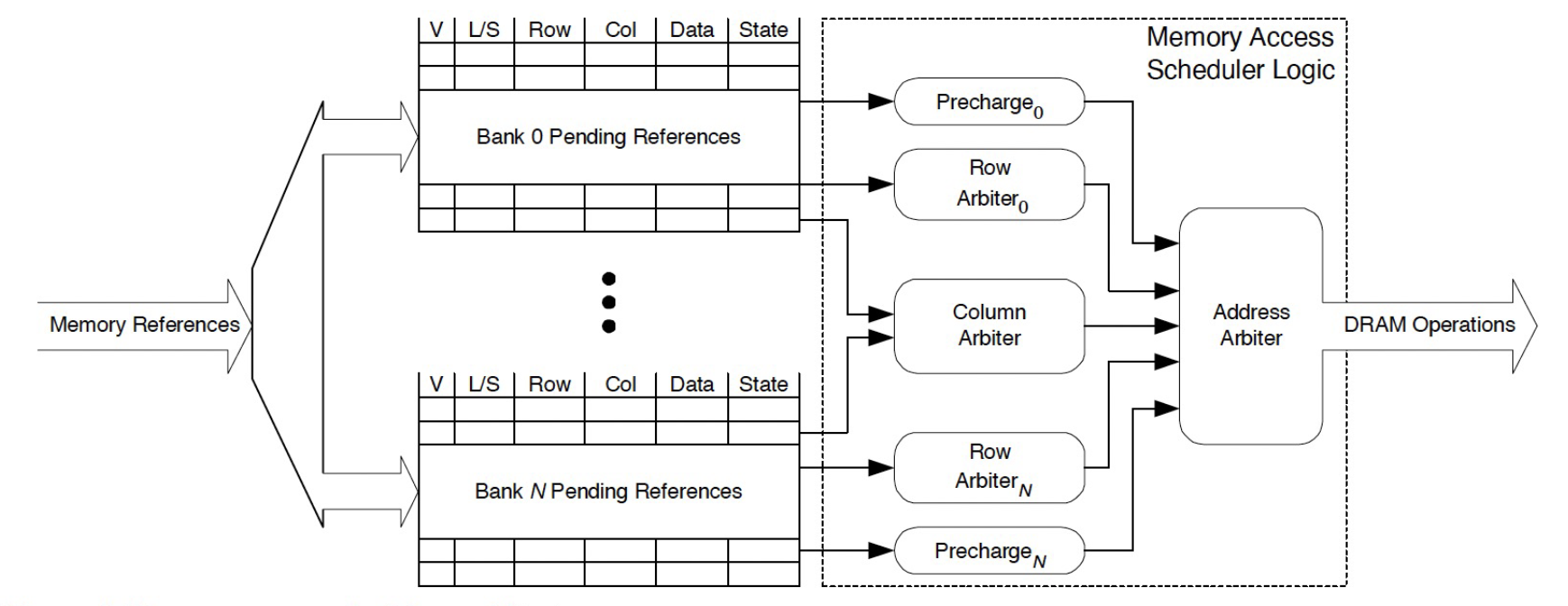
Because of this, the memory control has to maintain both a read queue and a write queue. A canonical memory controller is free to reorder the requests in these read and write queues. Based on some heuristics, one of these requests is selected as highest priority and moved into per-bank command queues. There is one of these queues per bank (associated with the channel).
The memory controller decomposes the request into multiple commands that are then placed into that bank’s command queue.
Decomposing Requests
For a request to an already open row, a single column read (CAS) command is enough to service the read request.
If the request causes a row conflict, then three commands are inserted into the command queue: precharge, activate(RAS), column-read(CAS)