This is a part of the Memory Subsystem.
Memory Dependences
Consider two memory instructions and . Generally, either a load ld <reg>, <addrmode>, or store st <reg>, <addrmode>.
Under what conditions are these instructions dependent?
Dependence through registers Dependence through memory
Various Cases
Let EA be the effective address of a register.
Precondition
- No such that and
- Uniprocessor
Read After Read Case
- We can reorder instructions
- Value from one load can be forwarded to the other load
Write after Read
We cannot reorder instructions in this case.
Read After Write
We cannot reorder instructions, but we can forward the value from the memory stage of the first instruction to the second.
Write After Write
We cannot reorder instructions, but there is a possibility to omit the first store.
Concepts of the Load Store Queue
LSQ sends loads and stores to the memory subsystem.
Loads can execute immediately, kinda...
Even if you know the effective address of a load, if there is a store ahead that is unresolved, we can’t know if that store is writing to the same address or a different address
Stores must wait until we are sure that it is safe to update processor state.
| Type | Direction | Action: Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Loads | Search all the stores before | 1. Terminate and forward value: Store to the same address found 2. Terminate: Store with an unresolved address found 3. Go to D$: Conditions 1 and 2 not met |
| Stores | Search all the stores after | 1. Terminate: Store to the same address found 2. Terminate: Store with an unresolved address found 3. Forward value: Load from the same address found |
Implementation of the Load Store Queue
For efficiency, use two queues, one load and one store. The queues are circular.
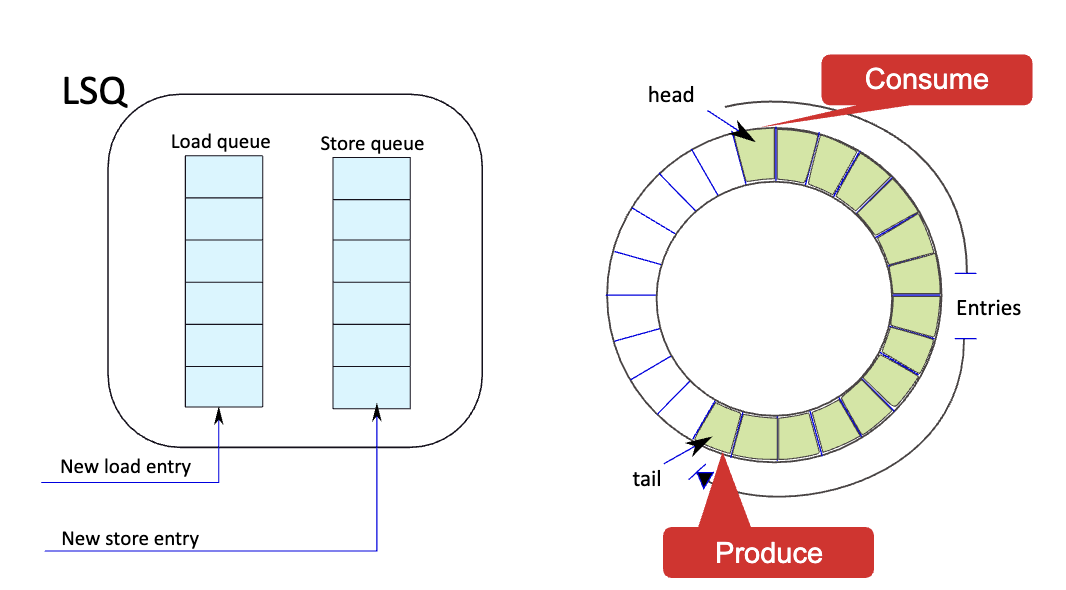
There are a lot of operations that can happen at each cycle:
- Compute various functions and find a set of queue locations of interest
- Find either the first or last location
- Enqueue and dequeue memory operations
- Resolve memory operations on completion of EA calculation
- Handle limited queue size